Renercycle is advancing with technologies to recover complex materials such as blades and a strategy for expansion in Europe and Asia, while the sector seeks to accelerate projects amid regulatory barriers.
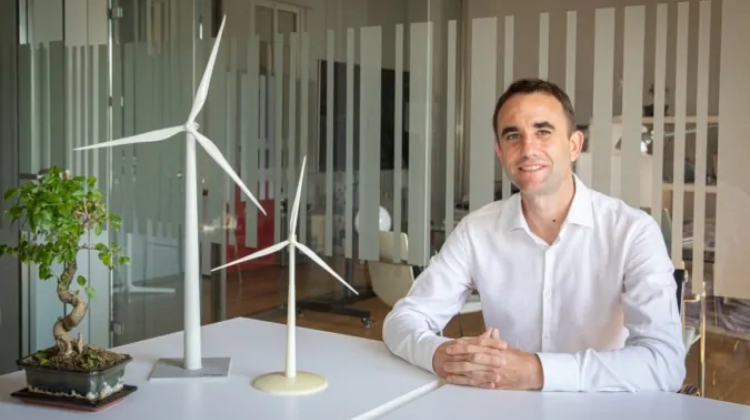












Renercycle is advancing with technologies to recover complex materials such as blades and a strategy for expansion in Europe and Asia, while the sector seeks to accelerate projects amid regulatory barriers.

With the potential to generate up to 120 GW of offshore wind power and store 78 billion tonnes of CO₂, the UK-Norway alliance strengthens Europe’s energy security, opens investment opportunities, and promises the creation of up to 51,000 clean energy jobs.

The UK is making a decisive leap in its clean energy transition as The Crown Estate launches its Capacity Increase Programme, adding 4.7 GW of renewable capacity across seven offshore wind farms. This initiative will supply clean energy to up to four million homes, while enhancing energy security and supporting the country’s decarbonisation goals.

The Spanish Wind Energy Association (AEE) presented a new initiative at the Congress of Deputies aimed at giving a voice to residents of municipalities with wind farms. The forum includes a book featuring over 50 testimonies and aspires to become a permanent dialogue platform.

Future Energy Summit (FES) Iberia 2025 will bring together more than 400 executives from the public and private sectors on June 24 at the Colegio de Caminos, Betancourt Auditorium, in Madrid. They will share the space with industry leaders such as Repsol, Galp, and Sonnedix, at an event that will bring together more than 400 executives to discuss key trends in the energy market.

Robert Francis Prevost has been elected as the new Pope, adopting his name in homage to the Church’s progressive tradition. This, together with his close relationship with Francis, could signal a continuation of support for renewable energy and sustainability.

According to the Swedish Energy Agency, electricity production will increase by 15% by 2028, driven by wind and nuclear power. Despite geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainty, industrial demand is set to rise by 25%, primarily due to green hydrogen projects.
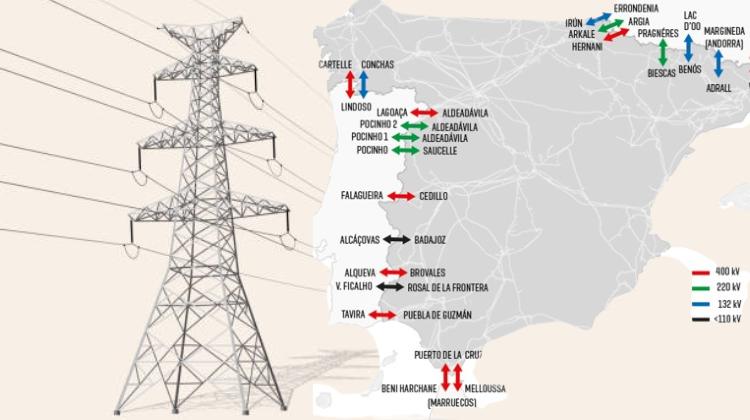
REN reinstates the energy flow from Spain with a 1,000 MW cap following the 28 April blackout, in place until 12 May.

The 28 April’s power outage exposed the fragility of Spain’s power system. Fundación Renovables proposes five concrete measures—from strengthening storage to demand-side flexibility—to prevent setbacks in the transition towards a decarbonised and 100% renewable model.

Electrical engineer Nayeem Hossain analyzes the progress of marine renewable energy, from offshore wind to tidal power and hybrid solutions. He asserts that, although the market is still developing, the potential is “immense” and could transform the European electricity system.

The last month closed with 24 PPAs signed and 1.45 GW contracted across Europe. Onshore wind led the market, and contract sizes doubled compared to January, consolidating a new dynamic during the first four months of 2025

The Department for Energy Security & Net Zero has confirmed regulatory changes to the Contracts for Difference (CfD) scheme ahead of Allocation Round 7 (AR7), including later publication of the budget, expanded access to anonymised bid data for the Secretary of State, and integration of the Clean Industry Bonus into Ofgem’s price cap.

He recommends exercising extreme caution with traditional renewable investments and anticipating the business of energy storage and grid stabilisation.

Poland’s share of renewables in its electricity mix has grown from 8% in 2015 to 30% in 2024. With new auctions, regulatory easing and a booming solar segment, the country now aims to reach 56% by 2030, according to insights from LevelTen Energy.

FES Iberia 2025 will explore how to strengthen energy security in the aftermath of the blackout, analysing the role of storage, grids and regional integration in systems with high renewable penetration and increasing operational complexity.

Polish energy group ORLEN is advancing Baltic Power, the country’s first offshore wind farm, which will be operational in 2026 and cut CO₂ emissions by 2.8 million tonnes annually. It also aims to reach 12.8 GW of installed renewable capacity by 2035, including storage and five new offshore projects.

Minister Darragh O’Brien has announced the launch of the National Designated Maritime Area Plan (DMAP), aimed at centralising offshore renewable energy planning and providing certainty for the sector to meet the 2040 target of 20 GW. “This maximises our financial, human and time resources,” states the Minister.

The President of AELĒC (Asociación de Empresas de Energía Eléctrica), Marina Serrano, has issued a formal statement regarding the investigation initiated by MITECO (Ministry for the Ecological Transition and the Demographic Challenge) into the widespread power outage that occurred on Monday.

Faced with an electricity system increasingly dominated by renewable energy and inverters, the United Kingdom is redefining its approach to system recovery after major blackouts. The strategy now includes storage, regional restart pathways and a decentralised infrastructure, as analysed by Dlzar Al Kez, Research Associate at Net Zero Infrastructure, in conversation with Strategic Energy Europe.

The discussions concerned the objectives and values of the European Climate Adaptation Plan, the role of technology in accelerating eco-innovation and the need to involve the private sector in climate action, inter alia.

At the Three Seas Summit, Sebastian Burduja and Christopher Allen Wright held the first official meeting between energy ministers from both countries, reaffirming their strategic cooperation on projects such as SMR, Cernavodă, and renewable energy. Furthermore, Romania has surpassed 2.1 billion lei in photovoltaic investments for local entities.

Renercycle is advancing with technologies to recover complex materials such as blades and a strategy for expansion in Europe and Asia, while the sector seeks to accelerate projects amid regulatory barriers.

With the potential to generate up to 120 GW of offshore wind power and store 78 billion tonnes of CO₂, the UK-Norway alliance strengthens Europe’s energy security, opens investment opportunities, and promises the creation of up to 51,000 clean energy jobs.

The UK is making a decisive leap in its clean energy transition as The Crown Estate launches its Capacity Increase Programme, adding 4.7 GW of renewable capacity across seven offshore wind farms. This initiative will supply clean energy to up to four million homes, while enhancing energy security and supporting the country’s decarbonisation goals.

The Spanish Wind Energy Association (AEE) presented a new initiative at the Congress of Deputies aimed at giving a voice to residents of municipalities with wind farms. The forum includes a book featuring over 50 testimonies and aspires to become a permanent dialogue platform.

Future Energy Summit (FES) Iberia 2025 will bring together more than 400 executives from the public and private sectors on June 24 at the Colegio de Caminos, Betancourt Auditorium, in Madrid. They will share the space with industry leaders such as Repsol, Galp, and Sonnedix, at an event that will bring together more than 400 executives to discuss key trends in the energy market.

Robert Francis Prevost has been elected as the new Pope, adopting his name in homage to the Church’s progressive tradition. This, together with his close relationship with Francis, could signal a continuation of support for renewable energy and sustainability.

According to the Swedish Energy Agency, electricity production will increase by 15% by 2028, driven by wind and nuclear power. Despite geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainty, industrial demand is set to rise by 25%, primarily due to green hydrogen projects.

REN reinstates the energy flow from Spain with a 1,000 MW cap following the 28 April blackout, in place until 12 May.

The 28 April’s power outage exposed the fragility of Spain’s power system. Fundación Renovables proposes five concrete measures—from strengthening storage to demand-side flexibility—to prevent setbacks in the transition towards a decarbonised and 100% renewable model.

Electrical engineer Nayeem Hossain analyzes the progress of marine renewable energy, from offshore wind to tidal power and hybrid solutions. He asserts that, although the market is still developing, the potential is “immense” and could transform the European electricity system.

The last month closed with 24 PPAs signed and 1.45 GW contracted across Europe. Onshore wind led the market, and contract sizes doubled compared to January, consolidating a new dynamic during the first four months of 2025

The Department for Energy Security & Net Zero has confirmed regulatory changes to the Contracts for Difference (CfD) scheme ahead of Allocation Round 7 (AR7), including later publication of the budget, expanded access to anonymised bid data for the Secretary of State, and integration of the Clean Industry Bonus into Ofgem’s price cap.

He recommends exercising extreme caution with traditional renewable investments and anticipating the business of energy storage and grid stabilisation.

Poland’s share of renewables in its electricity mix has grown from 8% in 2015 to 30% in 2024. With new auctions, regulatory easing and a booming solar segment, the country now aims to reach 56% by 2030, according to insights from LevelTen Energy.

FES Iberia 2025 will explore how to strengthen energy security in the aftermath of the blackout, analysing the role of storage, grids and regional integration in systems with high renewable penetration and increasing operational complexity.

Polish energy group ORLEN is advancing Baltic Power, the country’s first offshore wind farm, which will be operational in 2026 and cut CO₂ emissions by 2.8 million tonnes annually. It also aims to reach 12.8 GW of installed renewable capacity by 2035, including storage and five new offshore projects.

Minister Darragh O’Brien has announced the launch of the National Designated Maritime Area Plan (DMAP), aimed at centralising offshore renewable energy planning and providing certainty for the sector to meet the 2040 target of 20 GW. “This maximises our financial, human and time resources,” states the Minister.

The President of AELĒC (Asociación de Empresas de Energía Eléctrica), Marina Serrano, has issued a formal statement regarding the investigation initiated by MITECO (Ministry for the Ecological Transition and the Demographic Challenge) into the widespread power outage that occurred on Monday.

Faced with an electricity system increasingly dominated by renewable energy and inverters, the United Kingdom is redefining its approach to system recovery after major blackouts. The strategy now includes storage, regional restart pathways and a decentralised infrastructure, as analysed by Dlzar Al Kez, Research Associate at Net Zero Infrastructure, in conversation with Strategic Energy Europe.

The discussions concerned the objectives and values of the European Climate Adaptation Plan, the role of technology in accelerating eco-innovation and the need to involve the private sector in climate action, inter alia.

At the Three Seas Summit, Sebastian Burduja and Christopher Allen Wright held the first official meeting between energy ministers from both countries, reaffirming their strategic cooperation on projects such as SMR, Cernavodă, and renewable energy. Furthermore, Romania has surpassed 2.1 billion lei in photovoltaic investments for local entities.

Select the sector you
want to know more about

The reform of Royal Decree 413/2014 provides relief for special-regime plants, removes barriers to battery integration, and redefines dispatch priority — generating positive expectations within the sector, albeit with nuances regarding its industrial impact.
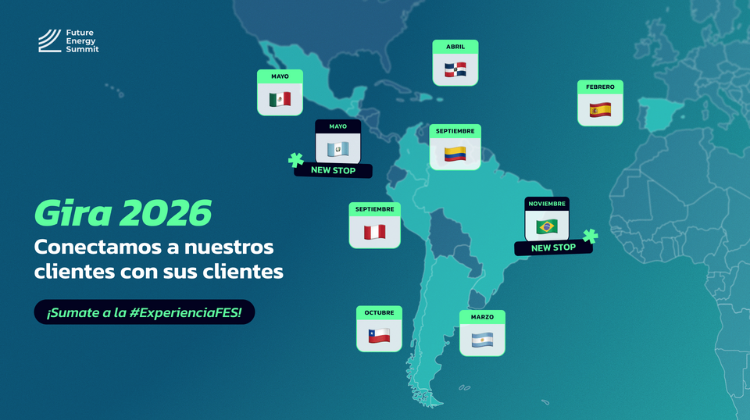
El próximo año de Future Energy Summit consolidará su presencia en mercados clave de Europa y América Latina con una agenda internacional que promueve alianzas estratégicas, innovación tecnológica y cooperación regional para acelerar la transición energética.

The next year of Future Energy Summit will consolidate its presence in key markets in Europe and Latin America with an international agenda that promotes strategic alliances, technological innovation and regional cooperation to accelerate the energy transition.