This agreement, established in partnership with OSW Netherlands, marks a significant step toward strengthening the supply of high-efficiency modules in the Dutch market.
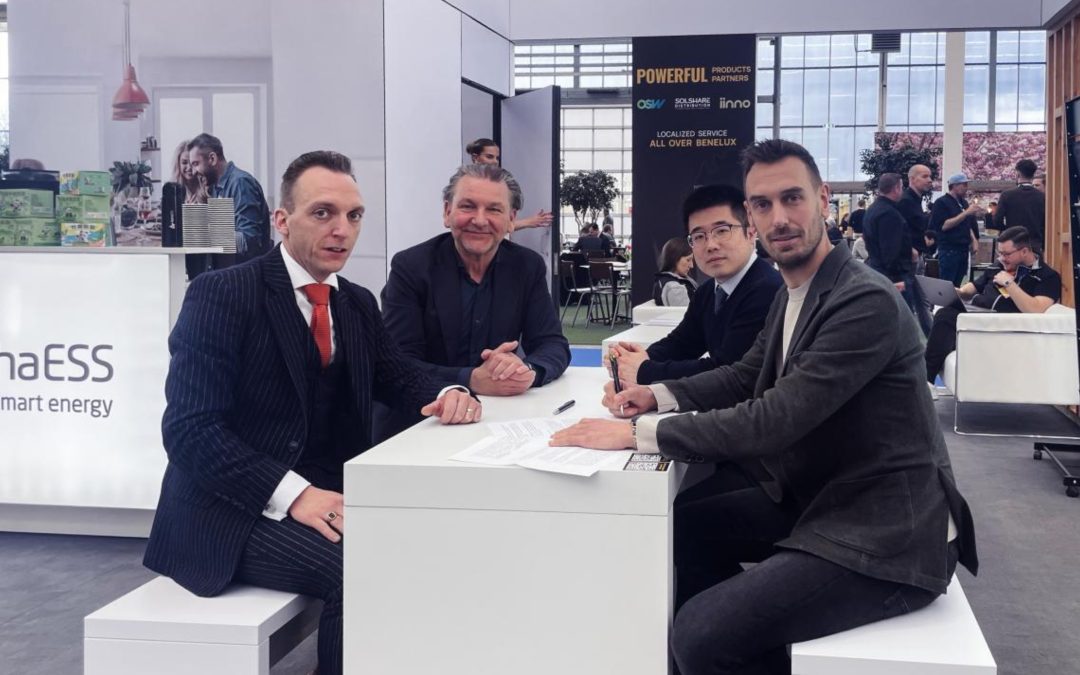












This agreement, established in partnership with OSW Netherlands, marks a significant step toward strengthening the supply of high-efficiency modules in the Dutch market.

In February 2025, Germany added 1,538 MW of renewable capacity, with solar photovoltaic accounting for 90% of the growth and onshore wind consolidating its recovery. According to the Bundesnetzagentur, the country is maintaining an expansion rate that brings it closer to its targets of 215 GW of solar and 115 GW of onshore wind by 2030.

In February 2025, 81.2% of Portugal’s electricity came from renewables, though generation fell by 5.1% due to lower wind production. Electricity prices rose by 77.6%, increasing reliance on imports. Emissions remained low, driven by strong hydropower generation.

The advancement of agrivoltaics requires greater versatility and new regulations. The company is committed to diversification, efficiency, and global manufacturing to remain competitive in a market impacted by Chinese pressure and trade changes in the United States.

Grid dispatch curtailment on solar energy have increased exponentially this year, impacting renewable energy development in the country. Preliminary data from EirGrid reveal that this trend is driven by network limitations, lack of storage, and electricity market regulations.

Meetings in Brussels with EU Commission representatives, focusing on environmental targets, biofuels, and renewable growth.

Francesco Marghella, an analyst, warns that auctions under the FER X schemes do not differentiate agrivoltaics from photovoltaics, which could limit its initial deployment. Moreover, current financial models ignore its agronomic value, a key factor for profitability. With the goal of reaching 7 GW by 2030, can Italy overcome these obstacles and unlock the potential of this technology?

Héctor Erdoician, CSO and CTO of Chemik, explains how the company optimizes its supply chain, develops proprietary technology, and expands in a highly competitive market.

The project will include the supply of over 1,400 1P solar trackers from Gonvarri Solar Steel, which will support 140,000 state-of-the-art solar modules.

The average time to connect a photovoltaic project to the grid in the European Union remains at four years, with delays extending up to eight years in some cases. This situation slows the deployment of renewable energy and generates additional costs for developers, compromising the region’s decarbonization goals.

The ministerial meeting was marked by discussions on affordable energy prices, energy security in the European Union, and the situation in Ukraine. Spain also endorsed a 90% emissions reduction target by 2040 and obtained approval for a €700 million aid scheme for energy storage.

Poland’s microinstallation sector reached a historic milestone in 2024, with more than 1.5 million units and a total installed capacity of 12.7 GW. Solar energy dominates the landscape, accounting for 99% of all installations. However, the sector’s rapid growth poses challenges for grid stability and the energy market.

The public consultation will be open until April 25, allowing interested parties to submit their comments on the proposed framework.

Luis Contreras, CEO of Yingli Green Energy Europe, discusses the impact of global production overcapacity, trade barriers, and the possibility of relocating panel manufacturing to the continent during the virtual event “Storage and Renewable Leadership Forum,” organized by Strategic Energy Corp.

Francesco Sassi, Research Fellow in Energy Geopolitics and Markets, warns in a conversation with Strategic Energy Europe that U.S. tariffs on Chinese solar products and the volatility of gas prices in the continent are shaping a new landscape of uncertainty in the renewable industry. Energy has become a political weapon, and the EU must decide between greater protection or commercial integration.

Terna has presented its 2025-2034 Development Plan, which will allocate more than 23 billion euros.The plan aims to integrate renewable energy sources, improve electricity transmission capacity, and expand international interconnections. Among the key projects are the Tyrrhenian Link, the Adriatic Link, and the energy bridge between Italy and Tunisia, which are pillars of the country’s decarbonization and energy security.

Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP) announced that its fifth flagship fund, CI V, has surpassed its €12 billion target at its final close.

During the Strategic Energy Forum, Ingenostrum called for a reform of energy pricing, highlighting that current volatility creates uncertainty and makes it difficult to sign PPAs.

The National Energy System Operator Limited (NESO) has confirmed the allocation of 43,055 MW in the T-4 capacity auction for the 2028/29 delivery year, with a clearing price of £60/kW/year. Conventional technologies dominated the awarded capacity, while battery storage and demand-side response (DSR) continued to gain ground.

The European Commissioner for Energy, Dan Jorgensen, stated that the EU could save up to 2.5 trillion euros by 2040 by deploying renewable energy more quickly. He emphasized that progress in the green transition has helped keep energy prices lower than they would have been. The strategy also focuses on reducing taxes, promoting long-term contracts, and improving energy system integration.

With 21,618 MW of photovoltaic capacity and 10,852 MW of wind farms as of early 2025, Poland continues to expand its renewable energy sector. However, the growing share of these sources in the electricity system raises challenges for market stability, including price fluctuations, grid congestion risks, and the need for better storage and demand management mechanisms.


This agreement, established in partnership with OSW Netherlands, marks a significant step toward strengthening the supply of high-efficiency modules in the Dutch market.

In February 2025, Germany added 1,538 MW of renewable capacity, with solar photovoltaic accounting for 90% of the growth and onshore wind consolidating its recovery. According to the Bundesnetzagentur, the country is maintaining an expansion rate that brings it closer to its targets of 215 GW of solar and 115 GW of onshore wind by 2030.

In February 2025, 81.2% of Portugal’s electricity came from renewables, though generation fell by 5.1% due to lower wind production. Electricity prices rose by 77.6%, increasing reliance on imports. Emissions remained low, driven by strong hydropower generation.

The advancement of agrivoltaics requires greater versatility and new regulations. The company is committed to diversification, efficiency, and global manufacturing to remain competitive in a market impacted by Chinese pressure and trade changes in the United States.

Grid dispatch curtailment on solar energy have increased exponentially this year, impacting renewable energy development in the country. Preliminary data from EirGrid reveal that this trend is driven by network limitations, lack of storage, and electricity market regulations.

Meetings in Brussels with EU Commission representatives, focusing on environmental targets, biofuels, and renewable growth.

Francesco Marghella, an analyst, warns that auctions under the FER X schemes do not differentiate agrivoltaics from photovoltaics, which could limit its initial deployment. Moreover, current financial models ignore its agronomic value, a key factor for profitability. With the goal of reaching 7 GW by 2030, can Italy overcome these obstacles and unlock the potential of this technology?

Héctor Erdoician, CSO and CTO of Chemik, explains how the company optimizes its supply chain, develops proprietary technology, and expands in a highly competitive market.

The project will include the supply of over 1,400 1P solar trackers from Gonvarri Solar Steel, which will support 140,000 state-of-the-art solar modules.

The average time to connect a photovoltaic project to the grid in the European Union remains at four years, with delays extending up to eight years in some cases. This situation slows the deployment of renewable energy and generates additional costs for developers, compromising the region’s decarbonization goals.

The ministerial meeting was marked by discussions on affordable energy prices, energy security in the European Union, and the situation in Ukraine. Spain also endorsed a 90% emissions reduction target by 2040 and obtained approval for a €700 million aid scheme for energy storage.

Poland’s microinstallation sector reached a historic milestone in 2024, with more than 1.5 million units and a total installed capacity of 12.7 GW. Solar energy dominates the landscape, accounting for 99% of all installations. However, the sector’s rapid growth poses challenges for grid stability and the energy market.

The public consultation will be open until April 25, allowing interested parties to submit their comments on the proposed framework.

Luis Contreras, CEO of Yingli Green Energy Europe, discusses the impact of global production overcapacity, trade barriers, and the possibility of relocating panel manufacturing to the continent during the virtual event “Storage and Renewable Leadership Forum,” organized by Strategic Energy Corp.

Francesco Sassi, Research Fellow in Energy Geopolitics and Markets, warns in a conversation with Strategic Energy Europe that U.S. tariffs on Chinese solar products and the volatility of gas prices in the continent are shaping a new landscape of uncertainty in the renewable industry. Energy has become a political weapon, and the EU must decide between greater protection or commercial integration.

Terna has presented its 2025-2034 Development Plan, which will allocate more than 23 billion euros.The plan aims to integrate renewable energy sources, improve electricity transmission capacity, and expand international interconnections. Among the key projects are the Tyrrhenian Link, the Adriatic Link, and the energy bridge between Italy and Tunisia, which are pillars of the country’s decarbonization and energy security.

Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP) announced that its fifth flagship fund, CI V, has surpassed its €12 billion target at its final close.

During the Strategic Energy Forum, Ingenostrum called for a reform of energy pricing, highlighting that current volatility creates uncertainty and makes it difficult to sign PPAs.

The National Energy System Operator Limited (NESO) has confirmed the allocation of 43,055 MW in the T-4 capacity auction for the 2028/29 delivery year, with a clearing price of £60/kW/year. Conventional technologies dominated the awarded capacity, while battery storage and demand-side response (DSR) continued to gain ground.

The European Commissioner for Energy, Dan Jorgensen, stated that the EU could save up to 2.5 trillion euros by 2040 by deploying renewable energy more quickly. He emphasized that progress in the green transition has helped keep energy prices lower than they would have been. The strategy also focuses on reducing taxes, promoting long-term contracts, and improving energy system integration.

With 21,618 MW of photovoltaic capacity and 10,852 MW of wind farms as of early 2025, Poland continues to expand its renewable energy sector. However, the growing share of these sources in the electricity system raises challenges for market stability, including price fluctuations, grid congestion risks, and the need for better storage and demand management mechanisms.
Select the sector you
want to know more about

During the AEGE Energy Forum 2025, industry representatives proposed a new model of three-party contracts between the public sector, energy producers and electro‑intensive consumers — a formula aimed at reducing volatility and accelerating decarbonisation.

Durante el Foro Energía AEGE 2025, los representantes del sector industrial propusieron un nuevo modelo de contratos a tres bandas entre el sector público, los productores de energía y los consumidores electrointensivos, una fórmula destinada a reducir la volatilidad y acelerar la descarbonización.
Photovoltaic production reached historic records for a single day in October in the main European markets, and wind energy also reached record levels in several of them. The increase in renewable generation, along with lower electricity demand in most markets and the drop in gas prices, were the main factors behind the price decline. For their part, CO2 futures reached their highest settlement price since mid-February, above €79/t, and Brent futures reached their lowest since the end of May.